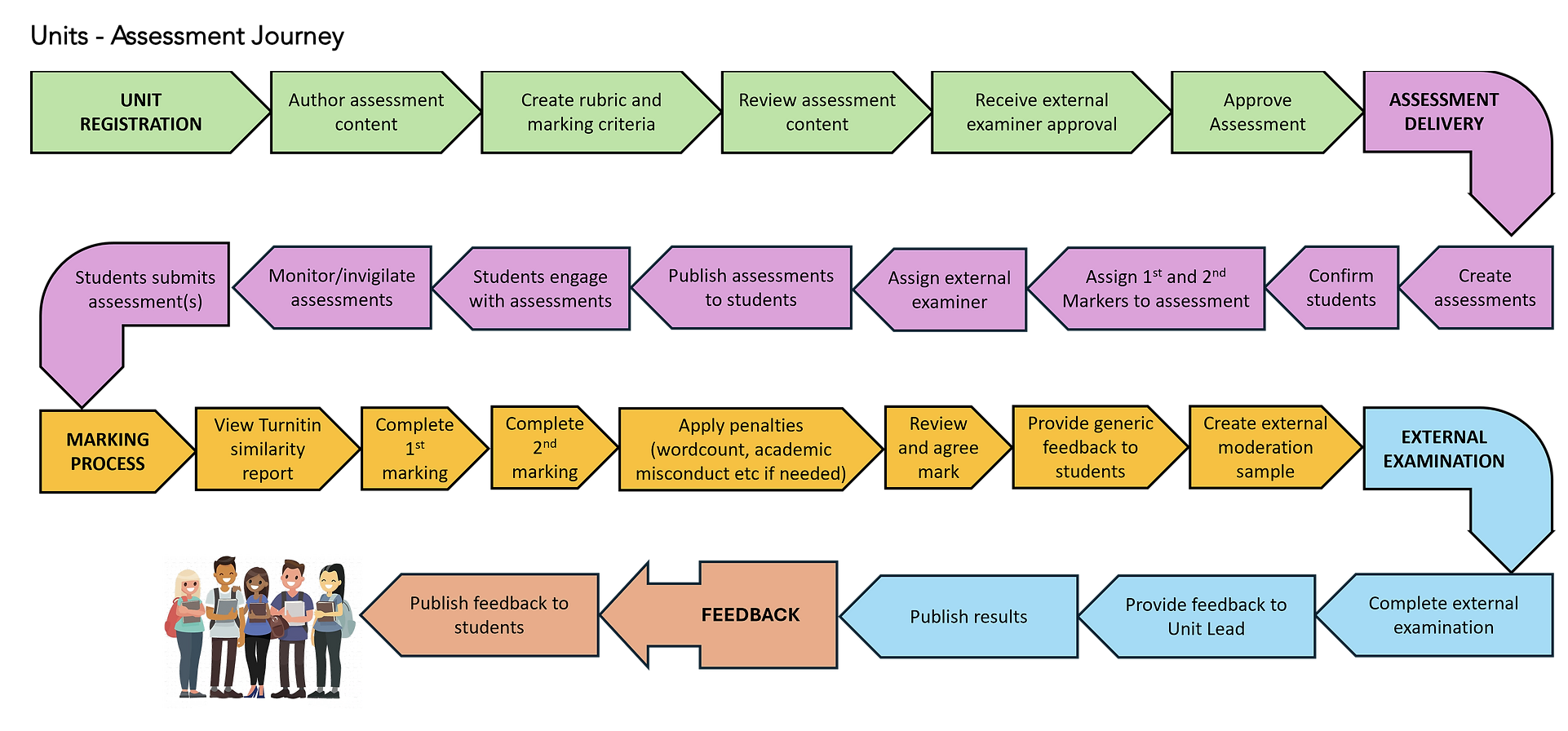
Assessment Hub
Quality assurance
‘Quality Assurance and Enhancement’ (commonly abbreviated as QA) refers to a collection of processes each School in the University is responsible for carrying out.
What is quality assurance?
Quality assurance and enhancement (commonly abbreviated as QA) refers to a collection of processes that are part of the University’s obligatory compliance with requirements set out by the Quality Assurance Agency (QAA) and the Scottish Credits and Qualifications Framework (SCQF). These public bodies are charged with implementing UK and Scottish Government policy concerning standards in higher education.
Full details of the University’s quality assurance procedures can be found on the Quality Framework webpages.
QA reporting and enhancement annual schedule
The Director of Quality, in consultation with the Curriculum and QA officer, the Undergraduate Director and the Graduate Director, produces, annually, a timetable for all QA procedures.
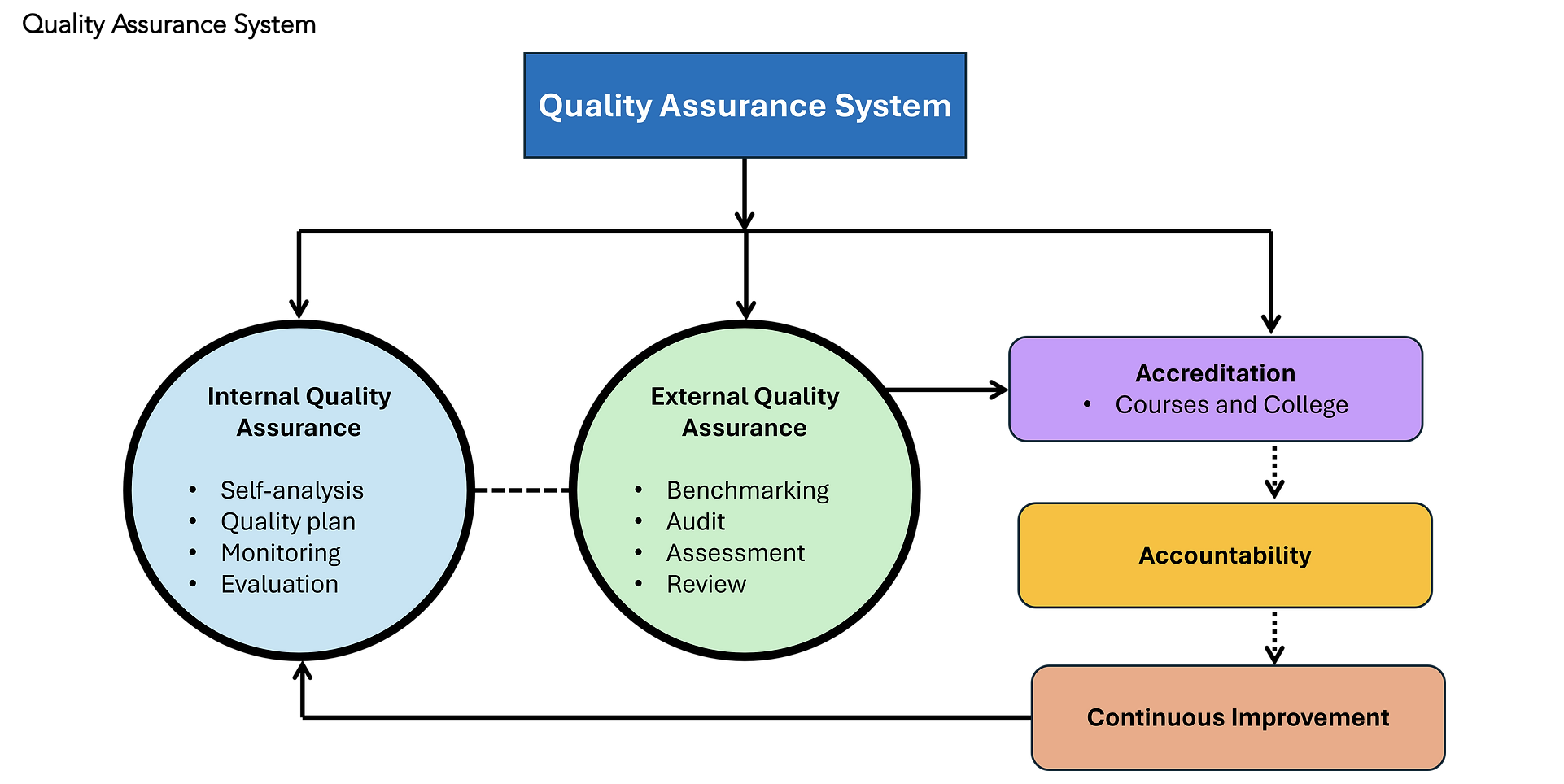
Internal Quality Assurance
The function of Internal Quality Assurance is to:
- Monitor the quality of assessment judgements.
- Ensure consistent and reliable assessment judgements are made across a provider.
- Highlight any problems, trends, and development needs of assessors.
- Ensure all procedures and policies within a provider are adhered to and maintained by staff.
Internal quality assurance measures learner achievements, assessor judgements, assessor knowledge and the standard of processes and procedures within a provider. This is in order to ensure learners can achieve qualifications, assessors are making the correct assessment judgements, and a provider is offering a high quality service. IQA activities also ensure staff working within a provider are qualified and competent.
Internal Quality Assurance Reviews:
- The knowledge, experience and competency of Assessors.
- How well learners meet the assessment criteria and learning outcomes of a qualification.
- The assessment judgements made by assessors.
- The standards of assessment and delivery sessions
- The records and reports kept by a provider, such as IQA Reports, sampling plans etc.
The four main elements related to internal quality assurance include:
- Sampling – Reviewing learner evidence and assessor judgements and feedback.
- Standardisation – Ensuring all assessors who deliver and assess on a qualification are doing so to the same standards.
- Observation – Observing assessor practice ensures that delivery and assessment of a qualification or course is done so to the correct standard.
- Feedback – Obtaining and analysing learner feedback on their experiences within a provider.
IQA includes monitoring the training and assessment activities and the quality of evidence learners produce. Internal quality assurance helps to ensure that assessments and IQA activities are valid, authentic, sufficient, fair and reliable.
Internal quality assurance measures the quality, delivery, processes, procedures and learner achievements.
Key Concepts and Principles of Internal Quality Assurance of Assessment include:
- Ensuring quality standards throughout the learner journey.
- Ensuring accuracy and consistency of assessment decisions made by assessors.
- Identifying issues and trends that develop.
- Supporting and developing assessors and tutors.
- Ensuring accountability for assessment decisions and quality standards, awarding body procedures and policies are maintained.
- Ensuring achievement made by learners and judged by assessors is recognised and meets the grading criteria.
- Ensuring the correct and appropriate assessment strategies are used by assessors.
- Ensuring confidently of the learner and provider are maintained at all times.
- Ensuring sampling both interim and summative is occurring.
Internal quality assurance principles include ensuring standardisation activities take place, assessment decisions embrace inclusion, equality is promoted with learners and the diversity of learners is valued by all staff. IQA ensures fairness is apparent in all assessment judgements and that clear and auditable records are held securely within a provider.
Other principles of IQA include maintaining health and safety practices, ensuring all centre employees have access to training and CPD activities. IQA must also ensure assessors and staff members are motivated and that clear communication between all provider employees takes place regularly.
External Quality Assurance
External Quality Assurance with UK Standing Committee for Quality Assessment (UKSCQA)
The external examining system has been a key mechanism for upholding academic standards in UK higher education for almost 200 years, ensuring comparability across different institutions. Within a system where autonomous institutions develop their own curricula, the UK higher education sector enables a vast range of courses to be offered which are linked to institutional research specialisms, local and industry needs, and student demand. External examiners perform an essential function in supporting this diversity of subjects, acting as constructively critical peers. For example, they support course teams to ensure that students are assessed fairly and transparently by offering independent advice and support on modes of assessment and learning outcomes.
External examiners form a pan-sector network across UK institutions, offering a wealth of intelligence about academic standards and the quality of provision. External examiners help to assess whether students meet the threshold academic standards set out in the UK Frameworks for Higher Education Qualifications. This is a significant part of the systematic quality framework that each institution operates and is often integral to the role of academic staff. These principles have been agreed by the UK Standing Committee for Quality Assurance (UKSCQA) and form an important addition to the Statement of Intent on Degree Classifications.1 They reiterate the value of appointing external examiners to work alongside UK institutions, thereby ensuring that students and the public can be confident that the degrees being awarded are a reliable and consistent reflection of graduate attainment. While they are not mandatory under any of the UK regulatory systems, they have been developed with and for the sector and have a strong role to play in protecting quality and standards. Therefore, the UKSCQA calls on institutions to commit to follow them and review their practices against them. The principles are directed at the two main stakeholders in the system: individuals performing the role, and the institutions that appoint them. Both institutions and individuals will benefit from considering the principles as a whole when operating the system. Institutions will also benefit from consulting the Quality Code Advice and Guidance on External Expertise. In addition, there are specific contexts for research provision recognised within the Quality Code Advice and Guidance on Research Degrees.
The principles can be used by higher education institutions and examiners to:
- Review processes and regulations in order to reinforce the essential role of the external examiner system in protecting UK academic standards and the value of qualifications over time.
- Support external examiners to carry out their role more effectively and transparently.
- Ensure that institutions achieve full value from the network of examiners who are engaged across the sector.




